Jejunostomy
Introduction
Jejunum is a part of small gut. Jejunostomy is the surgical procedure to insert a feeding tube into the jejunum. It is done if the patient cannot consume food through mouth. This path is used to introduce nutritious liquids and medicine when stomach is unable to receive food from mouth. This procedure is done in patients who are having difficulty in emptying stomach, who have pancreatic diseases or chances of aspirations of gastric contents into the lungs. This aspiration of fluid into the lungs may lead to fatal complications like pneumonia and death.
Before surgery the patient is examined and routine blood tests are prescribed to assess general health. Intravenous fluids and nutrition is provided to improve the general health. Since the conditions where jejunostomy is done usually lead to severe malnutrition, these measures are important before surgery to improve the post surgical outcome.
Duration of the hospital stay and recovery depends on the nature of the disease.
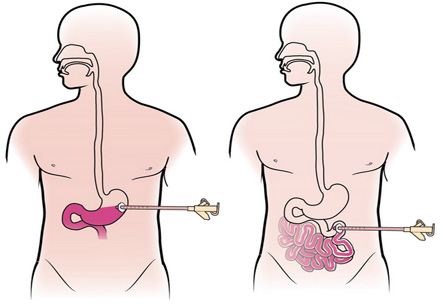
The patient is prepared for the surgery. The upper abdomen is shaved and cleaned with an antiseptic lotion. In most cases the surgery is done under general anesthesia. A stoma (hole) is made in the middle of the small gut to connect it to the exterior. It can be done as a open surgery or laparoscopic surgery. After the incision is made over the skin the jejunostomy tube is placed through the abdominal wall. An incision is also made on the jejunum and the tube is inserted. The tube is then secured well to avoid any complications like movement or dislodgement.
Duration of the hospital stay and recovery depends on the nature of the disease. After discharge from hospital the patient is advice to lead a restricted life initially. Intake of food and medicines should be carefully guided. Instructions of the doctor should be followed strictly. Initially antibiotics and pain medications are prescribed. Patient is taught how to care for the jejunostomy tube. Regular follow ups are essential for restoration of normal life and early detection of dislodgement or infection around the jejunostomy tube.